Compliance with EU Data Act

Compliance with EU Data Act
EU Data Act: Prepare for New Regulations
To foster the data economy in the European Union, EU legislators are currently reshaping business ground with new laws that shall enable fair and simple access to and use of data. The latest legislation: the EU Data Act, will become effective in September 2025.
With this deadline on the horizon, manufacturers of connected devices and others are required to act now. The timeline is tight, the obligations and requirements are ambiguous and fundamental business questions need to be clarified.
What is EU Data Act?
One important aspect of the EU Data Act is to grant users of connected products the right to access the generated machine data. In addition, the Data Act allows users to grant access to that data to third parties, which may be, for instance, independent service providers, AI startups and potentially also competitors.
Users and third parties may use the data for their own purposes, including providing third party service (as an alternative to manufacturer provided services) or analytics offers.
Manufacturers that fail to provide data access risk facing substantial financial penalties. The penalties shall be effective, proportionate and dissuasive and may have retroactive effect; if personal data is concerned, fines shall be according to the GDPR, which means the higher of EUR 20 million or 4% of the annual global revenue.
What is required and when?
Beside other obligations, manufacturers of connected products need to fulfill three key obligations by two deadlines.
- Information obligation
Starting from September 2025, manufacturers of connected products are required to inform users at point of sales about the data that the connected product generates during usage.
- Data sharing obligation
Starting from September 2025, the data holder (usually the manufacturer, if it chooses to collect the machine data) is required to share available data with the user of the connected product as well as with third parties authorized by the user.
- Design obligation
One year later, starting from September 2026, manufacturers must design new products in a way that the data is directly accessible to the user.
What do these obligations imply? Companies that sell connected products need to react now and start designing and implementing response strategies for sharing the relevant data. Yet, as is often the case, the details are where the real challenges lie.
Who does the law apply to?
The above-mentioned obligations under the EU Data Act apply to all manufacturers of connected products that make their products available in the EU, irrespective of their industry and place of establishment.
The right to access data is restricted to users within the EU. Third parties that were granted access by users must have a legal representation in the EU to be eligible for data access.
How can you become compliant?
The path to compliance is individual for each company, yet there are four key tips, from our experience, to make the journey a smoother one.
- Setting up a cross-functional team
Due to the complexity of this topic, different functions and experts from within the clients’ organization and from external need to be mobilized, including legal, government affairs, R&D, product management and IT. It is advised to involve all experts and concerned business units from day 1 to form a joint response strategy moving forward.
- 80/20 and risk-based approach
The Data Act applies not only to new products, but also to the existing installed base in many cases. Companies with a large variety of product families need to carefully plan their approach to balance the need of being compliant and the effort to implement.
- Close collaboration between legal and technology experts
Companies usually need to develop a new technical solution to fulfill the obligations under the Data Act. It is neither a pure technical nor an entire legal decision. Technical feasibility/effort and legal compliance risks need to be evaluated jointly to come up with an optimal solution. In addition, sales and customer service teams need to be involved as well to ensure a smooth customer experience.
- Treat this as a business opportunity rather than a pure compliance burden
Despite being a compliance topic from the first glance, the EU Data Act also provides vast opportunities for companies to capture. Creating new revenue streams of providing data, offering third party maintenance services for other companies’ products, or conducting AI analytics on competitors’ machine data, the opportunities seem endless.
How can Siemens Advanta help?
With our footprint in various industries and specifically our experience with the EU Data Act, we can support our clients on their way to become compliant with the obligations. Our project management services span from hands-on project management office support for urgent content issues, to developing comprehensive data strategies designed to meet future digital challenges. Siemens Advanta tailors its offerings and strategies to align with the unique needs and stages of development in areas, e.g. system architecture and data literacy, ensuring that our services are well-suited to each client's specific circumstances and objectives.
If you want to learn more about our offerings regarding the EU Data Act, please download the detailed presentation on the topic here:
Industry experts




Disclaimer
The information provided herein is for general informational and promotional purposes only and may not be accurate, complete or up to date. The information does not constitute any regulatory, legal, financial, technical or other professional advice.
No responsibility or liability will be accepted for any errors, omissions or inaccuracies in the content. Siemens Advanta disclaims, to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law, any and all liability or responsibility for the accuracy and completeness of the information contained herein and for any acts or omissions made based on such information. Siemens Advanta does not provide any legal, regulatory, audit, or tax advice; readers are responsible for obtaining such advice from their own legal counsel or other licensed professionals.
Cybersecurity in Hospitals

Cybersecurity in Hospitals
12 trends protecting the healthcare industry from cyber threats
Discover the 12 key trends in hospital cybersecurity, ranging from AI and machine learning to cloud security and IoT. Learn how cybersecurity awareness, data protection compliance, and managed security services play a crucial role in safeguarding the healthcare industry against cyber threats.
As the sophistication of cyberattacks continues to grow, the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks is becoming increasingly important.
The need for cybersecurity in hospitals is a top priority as hospitals are becoming increasingly reliant on technology, with electronic health records (EHRs), connected medical devices, and other digital systems now essential to patient care. This growing dependence on technology also makes hospitals more vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can have serious implications if preventative and curative measures are not taken.
As part of our commitment at Siemens Advanta to exploring this cutting-edge frontier in guarding against cyber theft, here are 12 crucial trends in healthcare cybersecurity that require careful attention.
These technologies are increasingly being used to detect anomalies in network traffic and respond quickly to potential threats.
The importance of cloud application and infrastructure security is increasing as hospitals increasingly adopt cloud services. To safeguard patient data, encryption technologies, strict access controls, and regular security checks are employed.
The growing connectivity of medical devices requires enhanced security measures to protect these devices from cyberattacks. Regular security updates and patch management, network segmentation, and the implementation of intrusion detection and intrusion prevention systems are effective in this regard.
Hospitals are investing more in staff training and awareness-raising to reduce human error and increase security awareness. The opening of phishing emails, insecure passwords and USB sticks are the focus here.
Hospitals are increasingly working with other organizations and authorities to share information about threats and security incidents and develop joint defense strategies.
The protection of end devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, is essential for cyber security in hospitals. New technologies such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) enable better detection and response to threats.
With the increasing use of telemedicine and mobile health applications, the need to protect these systems and applications against cyber attacks is also growing.
Hospitals must continue to ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as the GDPR and guarantee the protection of patient privacy.
Many hospitals opt for managed security services to outsource their IT security and focus on their core competencies. These services offer specialized expertise and continuous monitoring of security systems.
This plan should include clearly defined roles and responsibilities for the response team, establish communication protocols and provide a step-by-step guide for responding to security incidents.
This plan focuses on quickly restoring a hospital's critical systems and applications after a cyberattack or other disaster. It should include priorities for system and data recovery, recovery points and recovery times, and backup and recovery procedures.
Regular offsite backups and redundant systems can minimize the impact of cyberattacks and speed up recovery.
These trends provide a roadmap for healthcare institutions to strengthen their defenses by leveraging innovations such as AI and cloud security.
Navigating this complex terrain, concerted efforts to implement these trends will not only protect sensitive health data, but also strengthen the foundation of trust on which the healthcare system relies, ensuring a resilient and secure future for all.
Industry experts



AI Based Customer Journey in the Automotive industry

AI Based Customer Journey in the Automotive Industry
Optimize your customer journey based on AI
Knowing and fulfilling the needs of customers with the highest quality is the key to success in a customer-centric world. At the same time, digitalization has revolutionized the way how to interact with customers and how to improve customer experiences. At Siemens Advanta, we have developed an AI-based approach to optimize customer journeys.
Optimization of customer journey based on AI
The customer journey encompasses various stages, including Awareness, Search & Inform, Test, Purchase, Delivery, Usage, and Loyalization. Throughout this journey, customers interact with both digital (website or social media) and physical (showrooms, test drives, or dealerships) touchpoints.
In the context of the AI-based customer journey, the Analytics Engine plays a pivotal role as it serves as the AI-powered backbone, allowing for the intelligent suggestion of the "Next Best Activity". A learning analytics engine will orchestrate channels and touchpoints interplay to both optimize customer interactions and improve your business KPIs.
By continuously analyzing vast amounts of customer data, behavior patterns, and preferences, the Analytics Engine harnesses the power of AI to determine the most relevant and personalized actions. These suggestions empower companies to optimize interactions with customers based on their individual needs, thereby enhancing the overall customer experience and fostering lasting loyalty.
In the context of the AI-based customer journey, the Analytics Engine plays a pivotal role as it serves as the AI-powered backbone, allowing for the intelligent suggestion of the "Next Best Activity".
Moreover, the customer journey as a whole can be further enhanced through data-driven optimization and AI. By continuously analyzing customer data, interactions, and preferences, we can refine and improve the journey, ultimately elevating the overall customer experience. This will support you to improve Sales and Marketing effectiveness and efficiency.
Gaining deeper customer insights through AI can also help you improve other parts of your value chain, including the development of more customer-centric products and services.
Industry experts

Generative AI in Healthcare

Generative AI in Healthcare
Reshaping the Future of the Industry
Generative AI is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by leveraging its multi-modal power to automate, augment, and accelerate various work processes. With the ability to recognize learning patterns from large and diverse sets of unstructured data, generative AI is transforming healthcare in unprecedented ways.
Generative AI is trained on historic data and recognized learning patterns to generate outputs that are completely new. (1) This capability enables efficient content creation, allowing healthcare professionals to create personalized and informative content for patients. By tailoring educational materials and providing personalized recommendations, generative AI enhances the patient experience and improves healthcare outcomes. Furthermore, Generative AI can add value to the industry by automating, augmenting, and accelerating entire work processes.
Why should companies act now?
We witness an emergence of large-scale models since 2015 to deliver human-level and receive superhuman result. (2)
Bring more advanced computing approaches to the healthcare industry by unblocking GPUs' potential for training deep neural networks. (3)
Expanding the SaaS business model leads to a connection of hardware and software and the integration of cloud platforms with applications and services.
AI revolution is in full swing in unregulated industries with low barrier to enter.
AI as facilitator of new ways of working within three main pillars
- Pharma
- R&D processes to be made much more efficient by:
- Relieving scientists of time-consuming, repetitive tasks
- Accelerating the experiment ideation process
- Increasing the success rate of medication candidates
- MedTech
- AI accelerates the development of medical devices by:
- Avoiding the complex process of finding usable medical data
- Reducing the cost structure in the prototyping stage
- Redesigning and optimizing the development process in accordance with regulatory requirements
- Hospitals
- The patient experience and outcome in hospitals to be enhanced by:
- Optimizing diagnostic and treatment scheduling and administrative tasks
- Enhancing physicians with AI support in diagnosis and treatment suggestion
- Implementing patient and device tracking tools for better situational overview
- Optimizing the patient flow to create a seamless patient journey
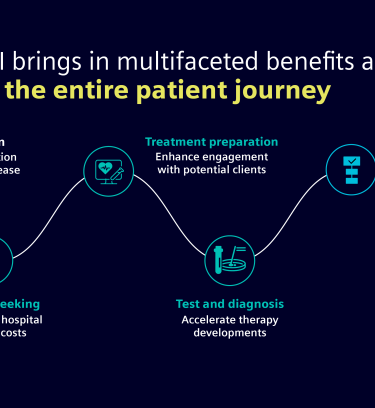
Impact throughout entire patient journey in healthcare
- Prevention
Assist medical staff in communicating treatment & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Treatment Management
Develop personalized treatment plans & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Clinical decision & treatment decision
Support diagnostic activities like medical images and lab tests - Test & Diagnosis
Collect & connect data to support patients via multi-lingual Chatbots that answer questions, offer advice and provide personalized recommendations - Symptom seeking & Treatment preparation
Create tailored content to educate and inform patients
Reducing Working Hours and Redesigning Roles with Patient-Centric Focus
The implementation of generative AI is set to have a significant impact on the tasks of medical assistants, while surgeons will experience less changes. By the year 2030, it is projected that automation could potentially reduce working hours by up to one-third across three key patient care activities. (4)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention.
Among these activities, patient management accounts for 32% of the potential reduction, followed by medical and clinical laboratory technicians at 21%, and surgery at 7%. However, realizing this automation potential relies on overcoming three key limitations.
- Job complexity as major limitation as high degrees of automation can only be achieved for very repetitive tasks currently
- The need for decision making within a job defines the framework for possible automating solutions
- Jobs associated with high risk (e.g., surgeons) face a lower degree of automation than lower risk jobs (e.g., medical assistants)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, healthcare workers can focus more on providing personalized care and making informed decisions that benefit the patients.
Firstly, Generative AI will reduce administrative tasks, allowing healthcare practitioners to dedicate more time to patient care. By automating administrative burdens, AI can streamline processes and free up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on providing personalized care. This can lead to higher job satisfaction and improved patient experiences.
Secondly, AI can support clinical activities by speeding up labor-intensive work and providing practitioners with valuable information. By analyzing large volumes of data and providing insights, AI can assist healthcare professionals in making more informed decisions, leading to enhanced patient outcomes and improved quality of care.
Lastly, AI enables easier access to a wealth of knowledge. By bringing vast amounts of relevant, curated, and prioritized knowledge to the fingertips of practitioners, AI opens up new possibilities for both learning and care delivery. This access to comprehensive information can empower healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest research and developments, ultimately benefiting patient care.
China dominates the market of artificial intelligence in healthcare
China benefits from strong government support and heavy investments in academic collaboration and startups. This has led to significant advancements in various industries, including healthcare. Chinese consumers have become increasingly aware of and accepting of digital AI solutions in different areas.
In particular, several Chinese tech leaders have emerged as major players in the healthcare sector. These companies have leveraged the country's supportive environment to develop innovative solutions and services. With their expertise in artificial intelligence and technology, they are transforming the healthcare landscape in China.
Europe's Progress in Healthcare AI
Europe is making substantial progress in key areas of healthcare AI and has established dedicated working groups (4)
Development of "The EU way" for AI with focus on transparent, ethical and trustworthy applications
AI adoption to be accelerated by linking healthcare information at the population level that can provide distinctive advantages
Private investments are increasing fast while having significant pan-European research strengths
Although, the lack of alignment and communication can hinder Europe's vision of becoming a leader in AI. While European investment and research in AI are strong when considered as a whole, they are fragmented at the country or regional level. This creates a complex environment where the approaches and aspirations of Member States need to be aligned, especially in areas such as healthcare digitalization where there are differences between countries like Estonia and Germany.
Furthermore, the further adoption of AI in Europe is being delayed due to a lack of linked datasets, which leaves critical issues such as data governance, access, and security unaddressed.
To overcome these challenges and achieve a seamless integration of AI into healthcare, there needs to be a continuous interplay between governments, scientists, and industry. Collaboration and coordination among these stakeholders are essential to ensure that Europe's AI initiatives are effectively implemented and aligned with its vision of becoming a leader in the field.
The Urgent Need for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
With the healthcare industry becoming increasingly digitized, the importance of cybersecurity has become more crucial than ever before. There are six key trends that highlight the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures in healthcare.
Firstly, the growing cyber risk to businesses poses a significant threat to the healthcare sector. As hackers become more sophisticated, healthcare organizations must stay one step ahead to protect sensitive patient data from cyberattacks.
Secondly, the lack of digitization in healthcare has created vulnerabilities in security systems. The transition to digital platforms and interconnected networks has exposed healthcare providers to potential breaches, making cybersecurity a top priority.
Thirdly, fundamental technological changes, such as the adoption of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), have expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. These advancements require enhanced security measures to safeguard critical healthcare infrastructure and patient information.
The fourth trend is the increasing professional hacking, where skilled hackers specifically target healthcare organizations for financial gain or to exploit sensitive data. This necessitates proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate risks and prevent data breaches.
Fifth, there is a surge in laws and regulations worldwide that aim to protect patient privacy and data security. Compliance with these regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, reinforces the need for robust cybersecurity practices in healthcare.
Lastly, the challenging landscape of local versus global regulations adds complexity to healthcare cybersecurity. Healthcare organizations must navigate the diverse regulatory requirements across different regions while ensuring the highest level of data protection.
Given these six key trends, it is clear that there is a strong need for immediate action to strengthen cybersecurity in the healthcare industry. Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures and staying updated with the latest technologies and best practices can help safeguard patient data, maintain trust, and ensure the delivery of quality healthcare services.
Siemens Advanta is committed to using AI as a catalyst of healthcare quality improvement by relying on Responsible AI
- Shape Sustainable development
Increase our positive economic, societal and environmental impact and thus contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. - Foster inclusiveness & shared benefit
Ensure diversity, fairness and inclusiveness by co-creating value for all stakeholders in a multidisciplinary approach. - Safeguard human oversight
The design of AI systems should always convey the objectives clearly defined by humans. - Guarantee data governance & privacy
Protect fundamental rights of partners, respecting their right to the protection and governance of personal and non-personal data. - Ensure system security & safety
Apply honest, credible, holistic rules and concepts as standards for security and safety. - Endorse explainability
Create awareness, trust and acceptance by explaining the rationale of AI solutions whilst safeguarding intellectual property. - Promote accountability & liability
Make policies and processes clear and accessible to guide stakeholders to take responsibility.
Key Takeaways on Generative AI in Healthcare:
- Generative AI has the potential to disrupt the healthcare ecosystem starting with repetitive administrative tasks but in the next 3-5yrs also reaching the core of healthcare diagnostics.
- Traditional health tech players as well as basic healthcare provider services are at risk to be disrupted by Big Tech companies utilizing Generative AI.
- To defend their leading market position, health tech players need to partner up with Big Tech to gain access to scarce Gen AI capabilities and gain speed and momentum.
Industry experts




- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier, McKinsey & Company
- Sevilla et al. (2022), Compute trends across three eras of machine learning, arXiv:2202.05924v2
- Chan HP, Hadjiiski LM, Samala RK. Computer-aided diagnosis in the era of deep learning. Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(5):e218-e227. doi: 10.1002/mp.13764. PMID: 32418340; PMCID: PMC7293164.
- Emerging AI and data driven business models in Europe, European Institute of Innovation & Technology
Agile Software Development

Agile Software Development
Sprint-based development of custom software solution
Siemens Advanta creates a software solution for the client’s business need, in an agile manner. Together with the client’s team, Siemens Advanta goes through the stages of problem discovery & target setting, details & aligns the objective, prototyping, solution design to business needs, proof of value, proof of real impact, productization, scaled implementation roadmap, and holistic scaling, including change management.
- Cooperative identification and assessment of problem statement and business demand
- Joint alignment of hypothesis and goal definition
- Agile sprint-based development of custom software solution
- Iterative validation of progress and achievements
- Tailored to client’s needs
- Transparent pricing model
- Co-creation approach to identify & validate business vision as basis for productization
We have thousands of developers working on the following topics:
- Vision Refinement Scoping
- Feasibility Studies
- Business Opportunity Development
- User Story Definition
- Technology Assessment
- Ref. Architecture
- Digital & IoT Strategy
- Design Thinking
- UX Design
- Solution Prototyping
- Conceptual Design
- Concept Validation
- Requirement Eng.
- UI Design
- Agile Project Setup
- Solution Architecture, Design & Customization
- Application Design & Development
- Systems Design
- Cloud Services
- OT Connectivity & Integration
- IT System Integration
- Platform Integration
- Enterprise Integration
- IT & OT Security
- Cybersecurity
- Machine Learning
- Computer Vision Analytics
- Predictive Maintenance
- Anomaly Detection
- Root Cause Analysis
- Data Visualization
- Real-Time Analytics
- Operate IoT Services and Solutions
- Maintaining Service Level Agreements (SLA)
- Continuous Solution Improvement
- Technical Support
- Customer Value Identification
- Customer Enablement
- Process Management
- Risk Management
- Quality Management
- Contract/ Subcontract Management
- Change Management
- Procurement Support/ Economies of Scale
Our industry leaders


Moving Smart Metering Data into the Cloud

Moving Smart Metering Data into the Cloud
Empowering utilities for a sustainable future
Leading solutions for end-to-end meter data management and cloud migration
Siemens Advanta's end-to-end, digital transformation services and solutions for utilities come with in-depth expertise in Meter Data Management implementation, customization, and seamless integration. These capabilities, paired with Azure certified cloud migration proficiency, made us the partner of choice for UK Power Networks' (UKPN) project to move its metering data into the cloud and to achieve operational excellence in digitalization - at scale.
See some of the capabilities we offer:
End-to-end solutions at scale: From conceptualization to implementation and ongoing support, we guide you through the entire journey of digital transformation.
Cloud migration expertise: Certified Azure partner ensuring a smooth transition of complex systems to the cloud.
Operational competence: Our teams provide continuous support and maintenance post-implementation, ensuring your systems operate at peak efficiency.
We are delighted with the seamless migration to Microsoft Azure. Moving to the cloud is also a key step towards enabling the country’s Net Zero transition. By building capacity to manage the increasing data from smart meters, we are ready for the growth of smart meters and low carbon technologies including electric vehicles and heat pumps.

Read full Press Release
Read the press release our client UKPN published on their successful MDM cloud migration project, with Siemens Advanta providing design, delivery and ongoing maintenance support services within this project.
Our industry leader

Driving digital transformation and open innovation with a strong ecosystem
Tune in to uncover what the world of open innovation ecosystem holds for the future.
How can cross-collaboration and open ideation help deal with industrial uncertainties? Get your answers from Aymeric Sarrazin and Peter Körte.
Find us also on your favorite Podcast APP:
Apple Podcast, Google Podcast, Siemens.fm,
Stitcher, Spotify (log in to listen on desktop)
Networks and Data Ecosystems Essential for the MedTech Industry’s Circular Future

Networks and Data Ecosystems Essential for the Medtech Industry's Circular Future
The concept of circular economy is not limited to only manufacturing or waste management sectors – it is crucial for every industry, especially MedTech and healthcare. Owing to increasing environmental damage and pollution rates caused by large corporations, other equally responsible sectors have been overlooked in the public domain.
MedTech is any technology used to save the lives of people suffering from a wide range of conditions. It can range from syringes and latex gloves to heart values and pacemakers or replacement joints for knees and hips to total body scanning machines.
The future of MedTech lies in the power of networks and data ecosystems, enabling the industry to build a circular and resilient healthcare ecosystem. Data ecosystems include various actors, like services, and software applications that use data to share and utilize it economically or socially. In many circular economy scenarios, this involves the network or the networking of companies. “By making these changes, transformation of the medical device industry to a more circular economy would advance the goal of providing increasingly complex care in a low-emissions future.”
What does a circular economy look like for MedTech?
In the following article we will provide experience-based insights on why MedTech companies must embrace networks and data ecosystems to navigate this complex landscape. Furthermore, we will show how companies managed to harness the power of connectivity and data-driven insights to meet the demands of a circular economy and beyond - ultimately thriving in a sustainable future.
Not If but when: Five reasons why the circular economy is crucial for MedTech
Even with these barriers, our experience shows that there are several significant reasons why MedTech companies need to invest in circularity, including:
- Regulatory compliance: By closing raw material loops and thereby reducing the product carbon footprint, the circular economy is a crucial element in a wide range of relevant frameworks and regulations (e.g., UN Sustainable Development Goals, Paris Agreement, Green Deal, etc.) and therefore an imperative to avoid fines and penalties.
- Resource Efficiency and Cost Savings: In times of rising material prices, using recycled or reclaimed materials leads to cost savings in raw material procurement, production, and waste management thereby improving the company's profitability and operational efficiency.
- Resilience and Supply Chain Stability: By reducing the dependence on scarce resources and minimizing vulnerability to price fluctuations or supply chain disruptions, circularity contributes to mitigating the risks associated with decoupling, climate change, resource depletion, and economic instability.
- Access to Sustainable Financing and Investors: Companies that embrace circularity are more likely to attract sustainable financing options and gain the interest of investors seeking companies with strong ESG performance, ultimately providing access to capital for growth and expansion.
- Development of new business models: Circularity drives companies to innovate in product design, business models, and operational processes leading to the generation of new revenue streams and services that provide ongoing revenue instead of relying solely on one-time sales.
Catena-X: The crossroads of data, infrastructure, and service
Let’s explore how circularity is improving industries like Automotive and ways in which we can apply these insights to the MedTech industry.
Increasingly stricter environmental regulations regarding electric mobility, rising prices of raw materials, and supply chain shortages provided an impetus/incentive for the German Association of the Automotive Industry (VDA) to start the development of Catena-X in 2020. This became one of the first and biggest circularity-focused digital ecosystems that connects companies throughout the automotive value chain.
The mission of Catena-X is to enable the digital flow of information across the entire supply chain from manufacturers to suppliers and service providers. Catena-X develops a digital map of the circular economy in the automotive industry - with more than 2,000 partners and across all levels of the value chain. This digital infrastructure enables secure and trusted end-to-end data exchange, facilitates supply chain optimization, supports new business models, and promotes innovation.
Data is a fundamental building block of the circular economy. It refers to the structured and standardized information exchanged within the ecosystem. This data includes product information, supply chain data, production data, vehicle data, and customer-related information. The data is collected, stored, and shared in a standardized format, enabling interoperability between different systems, and facilitating seamless collaboration between partners.
Another essential building block for the digital mapping of value-added processes over the entire life cycle in Catena-X is the European Union’s Digital Product Passport (DPP). This tool creates transparency and unlocks circularity proposed by the European Commission that will share product information across the entire value chain, including data on raw material extraction, production, recycling, etc. Digital product passports function as a holistic digital twin and play a crucial role in closing the information loop by providing actionable insights on ownership, materials, and lifecycle events.
The Battery Passport, a version of the DPP, represents the first use case of collecting information across different companies starting with the extraction of raw materials which was vital for Catena-X as it laid the groundwork for key issues in transparency and data availability. It even captured individual battery cells composition and high voltage storage. Moreover, it collected dynamic data from the use phase to the dismantling and recycling processes until the final life cycle stage.
The Battery Passport was key in facilitating the rapid scaling of sustainable, circular, and responsible battery value chains to meet the targets of the Paris Agreement through electrification of the transport and power sectors. And these accomplishments happened during the development state of the Battery Passport. In fact, a Battery Passport prototype was officially released by the Global Battery Alliance during the World Economic Forum’s Annual Meeting in Davos in January 2023.
The information collected is used for more precise calculation of reference values, the optimization of production processes and data-based decisions, (e.g., whether a battery can be used as stationary storage unit at the end of a vehicle's life cycle or which measures are suitable for achieving the highest possible recycling rate).
The infrastructure of Catena-X consists of the technical framework and digital infrastructure necessary to support data exchange and connectivity. It includes standardized communication protocols, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), cloud computing resources, and security measures. This infrastructure enables the seamless flow of data and information across different stakeholders in the automotive value chain.
With transparency along the value chain and the associated knowledge regarding the origin of materials as well as the product carbon footprint, Catena-X members are well prepared to tackle future regulations and are already seeing savings per year by avoiding import duties and penalty payments.
Catena-X also encompasses a wide range of value-added functionalities and applications built on top of the infrastructure and data components. These services include analytics, predictive maintenance, supply chain optimization, digital twin simulations, and other digital tools that enhance operational efficiency and decision-making. By leveraging shared data and infrastructure, these services enable stakeholders to gain insights, optimize processes, and create new business models.
In addition to the effects on productivity/savings, Catena-X enabled the pioneers of the battery passport to communicate with one voice to the government institutions and thereby influence the establishment of standards.
Connecting Catena-X to the MedTech industry
Our experience with Catena-X demonstrates that it is not a question of if - but rather of how quickly - one can start building comparable circular structures. It will indeed take time. In fact, it took three years to establish Catena-X as a case study for the circular economy despite this project having the highest prioritization at the board level, the establishment of cross-divisional teams, and the empowerment of IT systems. It is critically important to not underestimate the time needed to adequately ensure the network connectivity and data availability required to implement circularity in an industry.
Catena-X should serve as an example to the MedTech sector that companies can only succeed in meeting stricter requirements (such as CO2 emissions standards, recycling quotas, etc.), with the help of circular material and raw material cycles by working together with partners along the value chain.
The automotive industry shows that cooperation between OEMs and suppliers can happen and that continuous data flows can be established along the product life cycle thereby creating value for all involved. At the same time, it is evident that technologies such as digital twin or product passports play a decisive key role along with the alliance of companies.
Importantly, Catena-X serves as an example and lessons and proof of concepts learned from it, in our opinion, can be transferred and adapted to other industries. . Even though Catena-X has a strong focus on current activities in the EU, we believe the findings can also be applied to other regions such as the USA or APAC. Technologies and solutions such as the digital twin or product passports can be established and used independently of regional markets.
Making circularity a reality in MedTech
According to a recent Health Affairs report, “Transition to a circular economy begins with a commitment to high-value care. This broader framework can drive efficiency of facilities operations with respect to energy and waste management and can nudge clinicians to be mindful of resource consumption and to select environmentally preferable drugs and devices where choices exist. Adoption of such high-value principles in procurement will foster circular and ethical supply chains.”
But the transformation to a more sustainable or circular economy can’t just be for philanthropic reasons. There is a strong business case for these changes to ensure competitive advantages for MedTech companies.
Even if all the regulations and adoption drivers are not applicable to your organization today, turning a blind eye to the need to change will have adverse effects in the future. Decisions made today influence whether MedTech companies can contribute significantly to a sustainable healthcare system while remaining at the forefront of innovation.
Our contributors

Author


Advanced Analytics for Supply Chain Management

Advanced Analytics for Supply Chain Management
In an increasingly globalized economy, robust supply chain management is essential to meet customer demands, minimize costs, and mitigate risks. Our data-centric approach enables organizations to strengthen risk management, refine planning accuracy, and optimize working capital. By streamlining procurement processes, we uncover cost-saving opportunities and alternative sources. Through a blend of advanced analytics and industry expertise, we deliver tangible outcomes for our clients, driving operational efficiency, and reducing costs.
- Efficiently manage the supply chain through demand planning and inventory optimization
- Emphasis on operational excellence by identifying prime sources for improvement
- Streamline production operations, lead time, and distribution management for holistic improvements
- Boost forecasting accuracy by over 5%
- Enhance efficiency by reducing manual planning efforts by up to 80%
- Identify substantial savings potential through duplicate material analysis
- Lower average inventory and working capital requirements
- Reduce procurement costs and rapidly adapt to fluctuating price levels by improving transparency
- Access to accurate and high-quality data for advanced analytics implementation
- Cross-functional alignment on goals and efforts among procurement, logistics, finance, and IT
Industrial AI

Industrial AI
Industrial AI is revolutionizing the manufacturing landscape, enabling businesses to increase productivity and reduce costs. At Siemens Advanta, our deep expertise in the AI and IoT domains helps clients harness this technology to drive growth and competitiveness. We combine AI & IoT technology with digital consulting and domain know-how, integrating best practices from our own Siemens factories to provide customized solutions that optimize manufacturing processes and improve product quality.
- Advising industrial companies in defining and implementing their AI strategy
- Customized AI and IoT solutions tailored to the specific needs of each client
- Domain know-how, insights, and best practices from Siemens’ own factories
- Increased productivity and efficiency through optimized manufacturing processes
- Reduced costs and downtime by identifying areas of improvement
- Improved product quality through better process control and defect detection
- Enhanced decision-making through data-driven insights and predictive analytics
- Competitive advantage through the adoption of advanced AI and IoT technologies
- A culture of innovation and a commitment to continuous improvement
- A willingness to invest in the adoption of AI and IoT technologies to optimize manufacturing processes
- The ability to adapt to change and embrace new technologies
Our industry leader

Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page

 Download our brochure on the EU Data Act here
Download our brochure on the EU Data Act here