
Generative AI in Healthcare
Reshaping the Future of the Industry
Generative AI is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by leveraging its multi-modal power to automate, augment, and accelerate various work processes. With the ability to recognize learning patterns from large and diverse sets of unstructured data, generative AI is transforming healthcare in unprecedented ways.
Generative AI is trained on historic data and recognized learning patterns to generate outputs that are completely new. (1) This capability enables efficient content creation, allowing healthcare professionals to create personalized and informative content for patients. By tailoring educational materials and providing personalized recommendations, generative AI enhances the patient experience and improves healthcare outcomes. Furthermore, Generative AI can add value to the industry by automating, augmenting, and accelerating entire work processes.
Why should companies act now?
We witness an emergence of large-scale models since 2015 to deliver human-level and receive superhuman result. (2)
Bring more advanced computing approaches to the healthcare industry by unblocking GPUs' potential for training deep neural networks. (3)
Expanding the SaaS business model leads to a connection of hardware and software and the integration of cloud platforms with applications and services.
AI revolution is in full swing in unregulated industries with low barrier to enter.
AI as facilitator of new ways of working within three main pillars
- Pharma
- R&D processes to be made much more efficient by:
- Relieving scientists of time-consuming, repetitive tasks
- Accelerating the experiment ideation process
- Increasing the success rate of medication candidates
- MedTech
- AI accelerates the development of medical devices by:
- Avoiding the complex process of finding usable medical data
- Reducing the cost structure in the prototyping stage
- Redesigning and optimizing the development process in accordance with regulatory requirements
- Hospitals
- The patient experience and outcome in hospitals to be enhanced by:
- Optimizing diagnostic and treatment scheduling and administrative tasks
- Enhancing physicians with AI support in diagnosis and treatment suggestion
- Implementing patient and device tracking tools for better situational overview
- Optimizing the patient flow to create a seamless patient journey
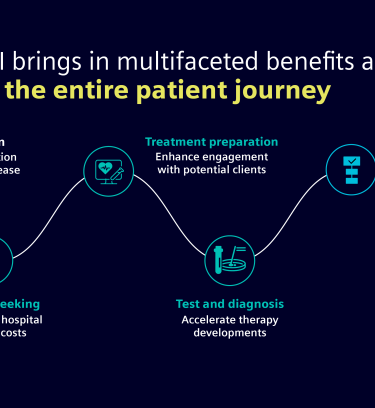
Impact throughout entire patient journey in healthcare
- Prevention
Assist medical staff in communicating treatment & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Treatment Management
Develop personalized treatment plans & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Clinical decision & treatment decision
Support diagnostic activities like medical images and lab tests - Test & Diagnosis
Collect & connect data to support patients via multi-lingual Chatbots that answer questions, offer advice and provide personalized recommendations - Symptom seeking & Treatment preparation
Create tailored content to educate and inform patients
Reducing Working Hours and Redesigning Roles with Patient-Centric Focus
The implementation of generative AI is set to have a significant impact on the tasks of medical assistants, while surgeons will experience less changes. By the year 2030, it is projected that automation could potentially reduce working hours by up to one-third across three key patient care activities. (4)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention.
Among these activities, patient management accounts for 32% of the potential reduction, followed by medical and clinical laboratory technicians at 21%, and surgery at 7%. However, realizing this automation potential relies on overcoming three key limitations.
- Job complexity as major limitation as high degrees of automation can only be achieved for very repetitive tasks currently
- The need for decision making within a job defines the framework for possible automating solutions
- Jobs associated with high risk (e.g., surgeons) face a lower degree of automation than lower risk jobs (e.g., medical assistants)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, healthcare workers can focus more on providing personalized care and making informed decisions that benefit the patients.
Firstly, Generative AI will reduce administrative tasks, allowing healthcare practitioners to dedicate more time to patient care. By automating administrative burdens, AI can streamline processes and free up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on providing personalized care. This can lead to higher job satisfaction and improved patient experiences.
Secondly, AI can support clinical activities by speeding up labor-intensive work and providing practitioners with valuable information. By analyzing large volumes of data and providing insights, AI can assist healthcare professionals in making more informed decisions, leading to enhanced patient outcomes and improved quality of care.
Lastly, AI enables easier access to a wealth of knowledge. By bringing vast amounts of relevant, curated, and prioritized knowledge to the fingertips of practitioners, AI opens up new possibilities for both learning and care delivery. This access to comprehensive information can empower healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest research and developments, ultimately benefiting patient care.
China dominates the market of artificial intelligence in healthcare
China benefits from strong government support and heavy investments in academic collaboration and startups. This has led to significant advancements in various industries, including healthcare. Chinese consumers have become increasingly aware of and accepting of digital AI solutions in different areas.
In particular, several Chinese tech leaders have emerged as major players in the healthcare sector. These companies have leveraged the country's supportive environment to develop innovative solutions and services. With their expertise in artificial intelligence and technology, they are transforming the healthcare landscape in China.
Europe's Progress in Healthcare AI
Europe is making substantial progress in key areas of healthcare AI and has established dedicated working groups (4)
Development of "The EU way" for AI with focus on transparent, ethical and trustworthy applications
AI adoption to be accelerated by linking healthcare information at the population level that can provide distinctive advantages
Private investments are increasing fast while having significant pan-European research strengths
Although, the lack of alignment and communication can hinder Europe's vision of becoming a leader in AI. While European investment and research in AI are strong when considered as a whole, they are fragmented at the country or regional level. This creates a complex environment where the approaches and aspirations of Member States need to be aligned, especially in areas such as healthcare digitalization where there are differences between countries like Estonia and Germany.
Furthermore, the further adoption of AI in Europe is being delayed due to a lack of linked datasets, which leaves critical issues such as data governance, access, and security unaddressed.
To overcome these challenges and achieve a seamless integration of AI into healthcare, there needs to be a continuous interplay between governments, scientists, and industry. Collaboration and coordination among these stakeholders are essential to ensure that Europe's AI initiatives are effectively implemented and aligned with its vision of becoming a leader in the field.
The Urgent Need for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
With the healthcare industry becoming increasingly digitized, the importance of cybersecurity has become more crucial than ever before. There are six key trends that highlight the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures in healthcare.
Firstly, the growing cyber risk to businesses poses a significant threat to the healthcare sector. As hackers become more sophisticated, healthcare organizations must stay one step ahead to protect sensitive patient data from cyberattacks.
Secondly, the lack of digitization in healthcare has created vulnerabilities in security systems. The transition to digital platforms and interconnected networks has exposed healthcare providers to potential breaches, making cybersecurity a top priority.
Thirdly, fundamental technological changes, such as the adoption of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), have expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. These advancements require enhanced security measures to safeguard critical healthcare infrastructure and patient information.
The fourth trend is the increasing professional hacking, where skilled hackers specifically target healthcare organizations for financial gain or to exploit sensitive data. This necessitates proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate risks and prevent data breaches.
Fifth, there is a surge in laws and regulations worldwide that aim to protect patient privacy and data security. Compliance with these regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, reinforces the need for robust cybersecurity practices in healthcare.
Lastly, the challenging landscape of local versus global regulations adds complexity to healthcare cybersecurity. Healthcare organizations must navigate the diverse regulatory requirements across different regions while ensuring the highest level of data protection.
Given these six key trends, it is clear that there is a strong need for immediate action to strengthen cybersecurity in the healthcare industry. Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures and staying updated with the latest technologies and best practices can help safeguard patient data, maintain trust, and ensure the delivery of quality healthcare services.
Siemens Advanta is committed to using AI as a catalyst of healthcare quality improvement by relying on Responsible AI
- Shape Sustainable development
Increase our positive economic, societal and environmental impact and thus contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. - Foster inclusiveness & shared benefit
Ensure diversity, fairness and inclusiveness by co-creating value for all stakeholders in a multidisciplinary approach. - Safeguard human oversight
The design of AI systems should always convey the objectives clearly defined by humans. - Guarantee data governance & privacy
Protect fundamental rights of partners, respecting their right to the protection and governance of personal and non-personal data. - Ensure system security & safety
Apply honest, credible, holistic rules and concepts as standards for security and safety. - Endorse explainability
Create awareness, trust and acceptance by explaining the rationale of AI solutions whilst safeguarding intellectual property. - Promote accountability & liability
Make policies and processes clear and accessible to guide stakeholders to take responsibility.
Key Takeaways on Generative AI in Healthcare:
- Generative AI has the potential to disrupt the healthcare ecosystem starting with repetitive administrative tasks but in the next 3-5yrs also reaching the core of healthcare diagnostics.
- Traditional health tech players as well as basic healthcare provider services are at risk to be disrupted by Big Tech companies utilizing Generative AI.
- To defend their leading market position, health tech players need to partner up with Big Tech to gain access to scarce Gen AI capabilities and gain speed and momentum.
Industry experts




- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier, McKinsey & Company
- Sevilla et al. (2022), Compute trends across three eras of machine learning, arXiv:2202.05924v2
- Chan HP, Hadjiiski LM, Samala RK. Computer-aided diagnosis in the era of deep learning. Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(5):e218-e227. doi: 10.1002/mp.13764. PMID: 32418340; PMCID: PMC7293164.
- Emerging AI and data driven business models in Europe, European Institute of Innovation & Technology

 Contact Us
Contact Us