Cybersecurity in Hospitals

Cybersecurity in Hospitals
12 trends protecting the healthcare industry from cyber threats
Discover the 12 key trends in hospital cybersecurity, ranging from AI and machine learning to cloud security and IoT. Learn how cybersecurity awareness, data protection compliance, and managed security services play a crucial role in safeguarding the healthcare industry against cyber threats.
As the sophistication of cyberattacks continues to grow, the practice of protecting systems, networks, and programs from digital attacks is becoming increasingly important.
The need for cybersecurity in hospitals is a top priority as hospitals are becoming increasingly reliant on technology, with electronic health records (EHRs), connected medical devices, and other digital systems now essential to patient care. This growing dependence on technology also makes hospitals more vulnerable to cyberattacks, which can have serious implications if preventative and curative measures are not taken.
As part of our commitment at Siemens Advanta to exploring this cutting-edge frontier in guarding against cyber theft, here are 12 crucial trends in healthcare cybersecurity that require careful attention.
These technologies are increasingly being used to detect anomalies in network traffic and respond quickly to potential threats.
The importance of cloud application and infrastructure security is increasing as hospitals increasingly adopt cloud services. To safeguard patient data, encryption technologies, strict access controls, and regular security checks are employed.
The growing connectivity of medical devices requires enhanced security measures to protect these devices from cyberattacks. Regular security updates and patch management, network segmentation, and the implementation of intrusion detection and intrusion prevention systems are effective in this regard.
Hospitals are investing more in staff training and awareness-raising to reduce human error and increase security awareness. The opening of phishing emails, insecure passwords and USB sticks are the focus here.
Hospitals are increasingly working with other organizations and authorities to share information about threats and security incidents and develop joint defense strategies.
The protection of end devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, is essential for cyber security in hospitals. New technologies such as Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) enable better detection and response to threats.
With the increasing use of telemedicine and mobile health applications, the need to protect these systems and applications against cyber attacks is also growing.
Hospitals must continue to ensure compliance with data protection regulations such as the GDPR and guarantee the protection of patient privacy.
Many hospitals opt for managed security services to outsource their IT security and focus on their core competencies. These services offer specialized expertise and continuous monitoring of security systems.
This plan should include clearly defined roles and responsibilities for the response team, establish communication protocols and provide a step-by-step guide for responding to security incidents.
This plan focuses on quickly restoring a hospital's critical systems and applications after a cyberattack or other disaster. It should include priorities for system and data recovery, recovery points and recovery times, and backup and recovery procedures.
Regular offsite backups and redundant systems can minimize the impact of cyberattacks and speed up recovery.
These trends provide a roadmap for healthcare institutions to strengthen their defenses by leveraging innovations such as AI and cloud security.
Navigating this complex terrain, concerted efforts to implement these trends will not only protect sensitive health data, but also strengthen the foundation of trust on which the healthcare system relies, ensuring a resilient and secure future for all.
Industry experts



Product Carbon Footprint

Product Carbon Footprint
Driving sustainability and reducing the environmental impact
In today's dynamic business landscape, sustainability has become a strategic imperative. Companies are under growing pressure to reduce and measure their product carbon footprint, meeting both regulatory mandates (e.g. EU taxonomy, corporate sustainability reporting directive) and the rising expectations of environmentally conscious consumers. This involves embracing sustainable practices, eco-friendly sourcing, and transparent reporting on their products’ carbon footprints.
A Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) is the result of measuring, managing, and communicating greenhouse gas emissions related to a product’s life cycle. The methodology used for calculating carbon footprints are life cycle assessments which analyze a product’s impact on climate change by analyzing CO2 emissions and CO2 emission equivalents (CO2e) over all life cycle stages.
(DIN EN ISO 14067 | Carbon footprint of product)
Challenges & complexity
Calculating the product carbon footprint for manufacturing companies can be a complex task, and several challenges are commonly encountered in the process. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Data collection, availability, and quality
Manufacturers may face outdated or incomplete data on raw materials, energy consumption, and other relevant factors. The absence of standardized formats further impedes comparability of carbon footprint calculations. -
Supply chain complexity
Global supply chains with multiple tiers of suppliers pose challenges in tracing material origins and accurately quantifying environmental impact. -
Scope 3 emissions
Scope 3 emissions encompass upstream and downstream emissions, contributing up to 90% of a product's CO2 value. However, companies often lack control over these emissions given their complex supply chains, making it challenging to include them in the calculation. -
Technology and methodology:
Selecting suitable tools and methodologies for carbon footprint calculations proves challenging, as different approaches can yield varying results. Staying updated on all evolving measurement standards, methodologies, and new technologies requires continuous effort. -
Regulatory compliance & reporting:
Meeting varying regional regulations and reporting standards further complicates carbon footprint calculations.
Leverage Siemens' state-of-the-art PCF solutions
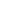
Siemens’ PCF ecosystem addresses the challenges of product-level carbon footprint calculations. Leveraging state-of-the-art technologies, we offer comprehensive solutions that go beyond compliance, fostering strategic sustainability positioning, and targeted PCF optimization along the entire value chain.
With its unparalleled expertise and industry-based approach, Siemens is the sole provider that possesses the domain know-how needed to tackle this pressing environmental challenge. By leveraging three PCF building blocks, empowered by Siemens-specific software tools and Siemens Advanta’s holistic consulting offering, we are driving the transformation towards a greener and more sustainable future.
Block 1: PCF Calculation – GreenDigitalTwin GDT (limited access)
Siemens’ GreenDigitalTwin (GDT) software is a powerful tool for businesses, offering accurate PCF calculations and a holistic understanding of environmental impact over the entire product lifecycle. Beyond PCF, Siemens' GDT enables comprehensive Life Cycle Assessments (LCAs) and the creation of Environmental Product Declarations (EPDs). Siemens' GreenDigitalTwin GDT is recognized as best-in-class, providing the necessary tools for informed decision-making and guiding companies towards sustainability goals by minimizing their carbon footprint.
Block 2: PCF aggregation along the supply chain – SiGREEN
At Siemens, we understand that true sustainability cannot be achieved in isolation. That is why Siemens developed SiGREEN, a software designed to securely aggregate emission data along the entire supply chain to generate dynamic PCFs based on true values. This means businesses can now gain insights into the environmental impact of their product lifecycle, including raw materials, manufacturing processes, transportation, and more. By visualizing the supply chain's carbon footprint, SiGREEN facilitates smarter decision-making and fosters collaboration between all stakeholders, driving the adoption of more sustainable practices across the board.
Block 3: PCF Governance – DigitalProductPass DPP
The final building block of Siemens’ PCF management approach is the DigitalProductPass DPP software. This innovative tool supports businesses in implementing a robust governance framework to ensure PCF compliance and transparency. The DigitalProductPass DPP enables companies not only to track, validate, and certify the PCF of their products, but it will also be a bullet-prove basis for future requirements like PCF-based taxation or the upcoming EU regulation.
Solutions: Driving sustainability through holistic Product Carbon Footprints
Siemens Advanta leads the way with cutting-edge solutions for product carbon footprints offering comprehensive consulting expertise. We empower businesses to quantify and manage their environmental impact and are your enabler for achieving PCF transparency and offers a wide range of tailored solutions:
Regulatory compliance guidance
Navigate environmental regulations with Siemens Advanta’s expertise, ensuring compliance and readiness for future standards. Furthermore, Siemens Advanta assists you in achieving official certifications for your PCFs, further increasing trust and transparency towards customers.
Carbon footprint capability
Empower clients to independently calculate product carbon footprints by providing and integrating state-of-the-art tools as well as providing comprehensive training.
Siemens Advanta provides you with the capabilities to accurately calculate your products’ carbon footprints.
Customized carbon reduction strategies
Develop tailored strategies to optimize supply chains, processes, reduce energy consumption, and minimize waste, surpassing compliance standards. Siemens Advanta is experienced in successfully leading decarbonization projects covering scope 1-3 emissions.
Green lean digital factory
Boost productivity, flexibility, and sustainability in production facilities. Our approach facilitates the transition to a streamlined, digital, and green "Factory of the Future" through scalable digital solutions, easing the transformation of people, processes, and technologies.
Product carbon footprint calculation (Scope 1-3)
Calculate your products’ carbon footprint, encompassing direct (Scope 1), indirect (Scope 2), supply chain, use-phase, and end-of-life (Scope 3) emissions by leveraging Siemens Advanta’s experts and PCF solution suite.
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) & Standardized Environmental Product Declaration (EPD)
Conduct extensive LCAs to provide you with even more insights regarding your product’s sustainability impact (e.g. water usage, energy consumption, biodiversity impact) and obtain third-party verified EPDs for your products to increase transparency towards consumers.
Siemens Advanta as your leader in a constantly evolving PCF environment
With its unique and comprehensive approach, Siemens Advanta revolutionizes the management of Product Carbon Footprints. By combining domain know-how, Siemens-specific software tools, and the expertise of Advanta, businesses can embark on a journey towards sustainability. From concept development to a full-blown implementation of customized solutions, Siemens Advanta's three PCF building blocks - PCF Calculation, PCF Aggregation, and PCF Governance - empower companies to make informed decisions based on real data, reduce their environmental impact, and contribute to a greener future. With Siemens Advanta, sustainability is no longer a distant goal but an achievable reality.
Industry experts


AI Based Customer Journey in the Automotive industry

AI Based Customer Journey in the Automotive Industry
Optimize your customer journey based on AI
Knowing and fulfilling the needs of customers with the highest quality is the key to success in a customer-centric world. At the same time, digitalization has revolutionized the way how to interact with customers and how to improve customer experiences. At Siemens Advanta, we have developed an AI-based approach to optimize customer journeys.
Optimization of customer journey based on AI
The customer journey encompasses various stages, including Awareness, Search & Inform, Test, Purchase, Delivery, Usage, and Loyalization. Throughout this journey, customers interact with both digital (website or social media) and physical (showrooms, test drives, or dealerships) touchpoints.
In the context of the AI-based customer journey, the Analytics Engine plays a pivotal role as it serves as the AI-powered backbone, allowing for the intelligent suggestion of the "Next Best Activity". A learning analytics engine will orchestrate channels and touchpoints interplay to both optimize customer interactions and improve your business KPIs.
By continuously analyzing vast amounts of customer data, behavior patterns, and preferences, the Analytics Engine harnesses the power of AI to determine the most relevant and personalized actions. These suggestions empower companies to optimize interactions with customers based on their individual needs, thereby enhancing the overall customer experience and fostering lasting loyalty.
In the context of the AI-based customer journey, the Analytics Engine plays a pivotal role as it serves as the AI-powered backbone, allowing for the intelligent suggestion of the "Next Best Activity".
Moreover, the customer journey as a whole can be further enhanced through data-driven optimization and AI. By continuously analyzing customer data, interactions, and preferences, we can refine and improve the journey, ultimately elevating the overall customer experience. This will support you to improve Sales and Marketing effectiveness and efficiency.
Gaining deeper customer insights through AI can also help you improve other parts of your value chain, including the development of more customer-centric products and services.
Industry experts

Cases Overview

Case Studies
Unlock the transformative power of IoT with real-world success stories: See how Siemens Advanta helped customers to achieve their goals on the journey to a full digital transformation.
- {{ filterActive.label }}
Generative AI in Healthcare

Generative AI in Healthcare
Reshaping the Future of the Industry
Generative AI is revolutionizing the healthcare industry by leveraging its multi-modal power to automate, augment, and accelerate various work processes. With the ability to recognize learning patterns from large and diverse sets of unstructured data, generative AI is transforming healthcare in unprecedented ways.
Generative AI is trained on historic data and recognized learning patterns to generate outputs that are completely new. (1) This capability enables efficient content creation, allowing healthcare professionals to create personalized and informative content for patients. By tailoring educational materials and providing personalized recommendations, generative AI enhances the patient experience and improves healthcare outcomes. Furthermore, Generative AI can add value to the industry by automating, augmenting, and accelerating entire work processes.
Why should companies act now?
We witness an emergence of large-scale models since 2015 to deliver human-level and receive superhuman result. (2)
Bring more advanced computing approaches to the healthcare industry by unblocking GPUs' potential for training deep neural networks. (3)
Expanding the SaaS business model leads to a connection of hardware and software and the integration of cloud platforms with applications and services.
AI revolution is in full swing in unregulated industries with low barrier to enter.
AI as facilitator of new ways of working within three main pillars
- Pharma
- R&D processes to be made much more efficient by:
- Relieving scientists of time-consuming, repetitive tasks
- Accelerating the experiment ideation process
- Increasing the success rate of medication candidates
- MedTech
- AI accelerates the development of medical devices by:
- Avoiding the complex process of finding usable medical data
- Reducing the cost structure in the prototyping stage
- Redesigning and optimizing the development process in accordance with regulatory requirements
- Hospitals
- The patient experience and outcome in hospitals to be enhanced by:
- Optimizing diagnostic and treatment scheduling and administrative tasks
- Enhancing physicians with AI support in diagnosis and treatment suggestion
- Implementing patient and device tracking tools for better situational overview
- Optimizing the patient flow to create a seamless patient journey
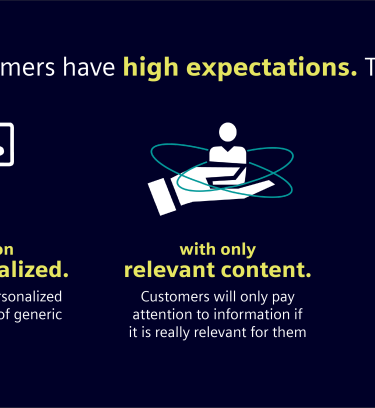
Impact throughout entire patient journey in healthcare
- Prevention
Assist medical staff in communicating treatment & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Treatment Management
Develop personalized treatment plans & automatically create & summarize diagnostic and other medical reports - Clinical decision & treatment decision
Support diagnostic activities like medical images and lab tests - Test & Diagnosis
Collect & connect data to support patients via multi-lingual Chatbots that answer questions, offer advice and provide personalized recommendations - Symptom seeking & Treatment preparation
Create tailored content to educate and inform patients
Reducing Working Hours and Redesigning Roles with Patient-Centric Focus
The implementation of generative AI is set to have a significant impact on the tasks of medical assistants, while surgeons will experience less changes. By the year 2030, it is projected that automation could potentially reduce working hours by up to one-third across three key patient care activities. (4)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention.
Among these activities, patient management accounts for 32% of the potential reduction, followed by medical and clinical laboratory technicians at 21%, and surgery at 7%. However, realizing this automation potential relies on overcoming three key limitations.
- Job complexity as major limitation as high degrees of automation can only be achieved for very repetitive tasks currently
- The need for decision making within a job defines the framework for possible automating solutions
- Jobs associated with high risk (e.g., surgeons) face a lower degree of automation than lower risk jobs (e.g., medical assistants)
Rather than replacing jobs altogether, the implementation of generative AI aims to redesign the way healthcare professionals work, placing patients back at the center of attention. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining processes, healthcare workers can focus more on providing personalized care and making informed decisions that benefit the patients.
Firstly, Generative AI will reduce administrative tasks, allowing healthcare practitioners to dedicate more time to patient care. By automating administrative burdens, AI can streamline processes and free up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on providing personalized care. This can lead to higher job satisfaction and improved patient experiences.
Secondly, AI can support clinical activities by speeding up labor-intensive work and providing practitioners with valuable information. By analyzing large volumes of data and providing insights, AI can assist healthcare professionals in making more informed decisions, leading to enhanced patient outcomes and improved quality of care.
Lastly, AI enables easier access to a wealth of knowledge. By bringing vast amounts of relevant, curated, and prioritized knowledge to the fingertips of practitioners, AI opens up new possibilities for both learning and care delivery. This access to comprehensive information can empower healthcare professionals to stay updated with the latest research and developments, ultimately benefiting patient care.
China dominates the market of artificial intelligence in healthcare
China benefits from strong government support and heavy investments in academic collaboration and startups. This has led to significant advancements in various industries, including healthcare. Chinese consumers have become increasingly aware of and accepting of digital AI solutions in different areas.
In particular, several Chinese tech leaders have emerged as major players in the healthcare sector. These companies have leveraged the country's supportive environment to develop innovative solutions and services. With their expertise in artificial intelligence and technology, they are transforming the healthcare landscape in China.
Europe's Progress in Healthcare AI
Europe is making substantial progress in key areas of healthcare AI and has established dedicated working groups (4)
Development of "The EU way" for AI with focus on transparent, ethical and trustworthy applications
AI adoption to be accelerated by linking healthcare information at the population level that can provide distinctive advantages
Private investments are increasing fast while having significant pan-European research strengths
Although, the lack of alignment and communication can hinder Europe's vision of becoming a leader in AI. While European investment and research in AI are strong when considered as a whole, they are fragmented at the country or regional level. This creates a complex environment where the approaches and aspirations of Member States need to be aligned, especially in areas such as healthcare digitalization where there are differences between countries like Estonia and Germany.
Furthermore, the further adoption of AI in Europe is being delayed due to a lack of linked datasets, which leaves critical issues such as data governance, access, and security unaddressed.
To overcome these challenges and achieve a seamless integration of AI into healthcare, there needs to be a continuous interplay between governments, scientists, and industry. Collaboration and coordination among these stakeholders are essential to ensure that Europe's AI initiatives are effectively implemented and aligned with its vision of becoming a leader in the field.
The Urgent Need for Cybersecurity in Healthcare
With the healthcare industry becoming increasingly digitized, the importance of cybersecurity has become more crucial than ever before. There are six key trends that highlight the urgency for robust cybersecurity measures in healthcare.
Firstly, the growing cyber risk to businesses poses a significant threat to the healthcare sector. As hackers become more sophisticated, healthcare organizations must stay one step ahead to protect sensitive patient data from cyberattacks.
Secondly, the lack of digitization in healthcare has created vulnerabilities in security systems. The transition to digital platforms and interconnected networks has exposed healthcare providers to potential breaches, making cybersecurity a top priority.
Thirdly, fundamental technological changes, such as the adoption of cloud computing and the Internet of Things (IoT), have expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. These advancements require enhanced security measures to safeguard critical healthcare infrastructure and patient information.
The fourth trend is the increasing professional hacking, where skilled hackers specifically target healthcare organizations for financial gain or to exploit sensitive data. This necessitates proactive cybersecurity measures to mitigate risks and prevent data breaches.
Fifth, there is a surge in laws and regulations worldwide that aim to protect patient privacy and data security. Compliance with these regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, reinforces the need for robust cybersecurity practices in healthcare.
Lastly, the challenging landscape of local versus global regulations adds complexity to healthcare cybersecurity. Healthcare organizations must navigate the diverse regulatory requirements across different regions while ensuring the highest level of data protection.
Given these six key trends, it is clear that there is a strong need for immediate action to strengthen cybersecurity in the healthcare industry. Implementing comprehensive cybersecurity measures and staying updated with the latest technologies and best practices can help safeguard patient data, maintain trust, and ensure the delivery of quality healthcare services.
Siemens Advanta is committed to using AI as a catalyst of healthcare quality improvement by relying on Responsible AI
- Shape Sustainable development
Increase our positive economic, societal and environmental impact and thus contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. - Foster inclusiveness & shared benefit
Ensure diversity, fairness and inclusiveness by co-creating value for all stakeholders in a multidisciplinary approach. - Safeguard human oversight
The design of AI systems should always convey the objectives clearly defined by humans. - Guarantee data governance & privacy
Protect fundamental rights of partners, respecting their right to the protection and governance of personal and non-personal data. - Ensure system security & safety
Apply honest, credible, holistic rules and concepts as standards for security and safety. - Endorse explainability
Create awareness, trust and acceptance by explaining the rationale of AI solutions whilst safeguarding intellectual property. - Promote accountability & liability
Make policies and processes clear and accessible to guide stakeholders to take responsibility.
Key Takeaways on Generative AI in Healthcare:
- Generative AI has the potential to disrupt the healthcare ecosystem starting with repetitive administrative tasks but in the next 3-5yrs also reaching the core of healthcare diagnostics.
- Traditional health tech players as well as basic healthcare provider services are at risk to be disrupted by Big Tech companies utilizing Generative AI.
- To defend their leading market position, health tech players need to partner up with Big Tech to gain access to scarce Gen AI capabilities and gain speed and momentum.
Industry experts




- The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier, McKinsey & Company
- Sevilla et al. (2022), Compute trends across three eras of machine learning, arXiv:2202.05924v2
- Chan HP, Hadjiiski LM, Samala RK. Computer-aided diagnosis in the era of deep learning. Med Phys. 2020 Jun;47(5):e218-e227. doi: 10.1002/mp.13764. PMID: 32418340; PMCID: PMC7293164.
- Emerging AI and data driven business models in Europe, European Institute of Innovation & Technology
Siemens Advanta Featured Articles

Siemens Advanta Featured Articles
Stay ahead of the curve with our expert-curated featured articles on the latest trends in IoT, offering you valuable insights and inspiration for embracing the digital revolution.
Read our latest featured article
Dynamics shaping the Dental Industry
Dental care is delivered via an ecosystem consisting of multiple players. Many a times, these players have overlapping products and capabilities which leads to competition for value across the chain.
Siemens Driving Sustainable Software Development

Siemens Driving Sustainable Software Development
Siemens Advanta as a leading force in green software innovation
Siemens is proud to announce its membership in the Green Software Foundation's steering committee, emphasizing a shared commitment to reducing software's environmental impact.
Why Siemens is committed
Software's Role in Sustainability: Siemens recognizes the pivotal role of software in advancing sustainability, aiming to invest in networks like Green Software Foundation (GSF) to drive change. GSF focuses on developing energy-efficient systems, striving to make green software the standrad for the future.

Read the Press Release
Read our press release to delve deeper into how Siemens is driving sustainable software development in collaboration with the Green Software Foundation.
Moving Smart Metering Data into the Cloud

Moving Smart Metering Data into the Cloud
Empowering utilities for a sustainable future
Leading solutions for end-to-end meter data management and cloud migration
Siemens Advanta's end-to-end, digital transformation services and solutions for utilities come with in-depth expertise in Meter Data Management implementation, customization, and seamless integration. These capabilities, paired with Azure certified cloud migration proficiency, made us the partner of choice for UK Power Networks' (UKPN) project to move its metering data into the cloud and to achieve operational excellence in digitalization - at scale.
See some of the capabilities we offer:
End-to-end solutions at scale: From conceptualization to implementation and ongoing support, we guide you through the entire journey of digital transformation.
Cloud migration expertise: Certified Azure partner ensuring a smooth transition of complex systems to the cloud.
Operational competence: Our teams provide continuous support and maintenance post-implementation, ensuring your systems operate at peak efficiency.
We are delighted with the seamless migration to Microsoft Azure. Moving to the cloud is also a key step towards enabling the country’s Net Zero transition. By building capacity to manage the increasing data from smart meters, we are ready for the growth of smart meters and low carbon technologies including electric vehicles and heat pumps.

Read full Press Release
Read the press release our client UKPN published on their successful MDM cloud migration project, with Siemens Advanta providing design, delivery and ongoing maintenance support services within this project.
Our industry leader

Green Hospital

Green Hospital
Building the future: Sustainable hospitals leading the way
In an era where health meets environmental consciousness, sustainability is getting more and more important. A study revealed that the CO2 emissions from healthcare in the world’s largest economies account for about 5% of their national carbon footprints, this is a larger share than either aviation or shipping.
Hospitals constitute a substantial portion of emissions within the healthcare industry. 64 % of energy consumption of all healthcare facilities is from large hospitals. To illustrate this further - one hospital bed in Germany requires more than twice the energy as an average household generating 64.4 tCO2e vs. 16.4 tCO2e, respectively. (Sources: MDPI; Universitätsklinikum Freiburg; Universitätsklinikum Freiburg; Our World in Data; Statista)
The primary contributors to greenhouse gas emissions within hospitals' operations are predominantly situated within their supply chains, necessitating targeted efforts for successful hospital decarbonization. According to the United Kingdom's National Health Service (NHS), a significant portion of the carbon footprint, accounting for 62%, is attributed to the supply chain, while only 24% of the hospital's carbon footprint falls under their direct control. (Source: The lancet)
Sustainable hospitals demand innovative solutions to embrace eco-friendly practices, reduce waste, cut energy bills, and improve patient care. For instance, sustainable hospitals can achieve energy savings through efficient lighting, HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. Additionally, sustainable hospitals often report higher patient satisfaction rates.
What's more, legislative support, driven by both sustainability and cost advantages, is propelling the demand for sustainable hospitals. The NHS in the UK, for instance, is pioneering an ambitious plan to become the world's first Net Zero National Health Service by 2045, aiming for an 80% reduction by 2039, and has earned recognition from the WHO as a leader in sustainable healthcare. Meanwhile, the U.S. Health Sector Climate Pledge is actively promoting the transition to sustainable hospitals, targeting a 50% reduction in GHG emissions by 2030 and net-zero hospitals by 2050, with 1,080 hospitals (15% of U.S. hospitals) already committed. This legislative pressure urges swift, cost-effective sustainable hospital initiatives to cut emissions. (Source: NHS England; HHS)
of the national carbon footprints in the world's largest economies are attributed to CO2 emissions from healthcare.
Source: Universitätsklinikum Freiburg
the primary contributors to greenhouse gas emissions in hospital operations are predominantly situated within their supply chains.
Source: United Kingdom's National Health Service (NHS)
of energy consumption of all healthcare facilities is from large hospitals.
Source: Universitätsklinikum Freiburg
more energy needed for one hospital bed in Germany compared to an average household's bed.
Source: Our World in Data
Sustainable hospitals demand innovative solutions to embrace eco-friendly practices.
Siemens has previously implemented substantial solutions to enhance sustainability in the healthcare sector:
- One success story by Siemens is exemplified by the recent Pfizer facility in Germany achieving a 40% increase in energy efficiency through the integration of Siemens technology and services. (Pfizer).
- Siemens further enhanced energy efficiency at Taiwan's Development Center for Biotechnology (DCB) by introducing advanced controls for chilled water pumps and cooling water pumps, resulting in an impressive energy savings rate of 21.7%. (Taiwan Biotechnology Development Center).
- Another notable success story occurred at the Reutte Hospital in Austria, where Siemens transformed Reutte into a sustainable hospital by renovating the heating system and using a photovoltaic system on the roof with target energy savings of more than €150,000 per year (Reutte).
Our 3-step process for the "Green Hospital of the Future" initiative
Phase 1: Assessment - This phase involves diagnosing the patient's needs and requirements.
Phase 2: Conceptualization - Here, we create a comprehensive treatment plan based on the assessment.
Phase 3: Program Implementation - In this final phase, we execute the treatment plan and continuously monitor the patient's progress.
Industry experts



Circularity Vehicle Passport

Circularity Vehicle Passport
The automotive industry at the forefront of circularity – a digital transformation
Digital product passports are a core element in the circular economy strategy of the European Union Green Deal.
In the upcoming years, we will see an increasing number of products to be accompanied with digital collections of their individual specifications and characteristics. With this, the EU aims to improve transparency for consumer decisions and all players along the value chain, to promote sustainable products and enable new circular business models.
The greater context – EU Green Deal & the automotive industry
On the path to fight climate change, circularity becomes increasingly prominent within the European Union and its member states. In fact, the European Green Deal declared circularity as one of the main pillars to drive sustainability. This implies that Europe’s major industries need to strive for increasing circular practices within their operations. The automotive industry is set to be one of the key areas for action, claiming the highest resource consumption within the EU as well as relying on an extensive value chain, impacting many other industries. Vehicle production is responsible for 19% of the steel consumption within the EU as well as for 10% of plastics used. Hence, legislators are evaluating measures to drive circular developments within the automotive industry in the context of the European Green Deal. (6)

Siemens Battery Passport
Our colleagues from Siemens are actively developing a Battery Passport ecosystem that goes beyond regulations. It empowers stakeholders to access and manage battery value chain data, using customizable add-on applications for analytics, sustainability, and more. This ecosystem is designed for universal accessibility and seamless integration with existing platforms, ensuring a user-friendly experience along the value chain. Join us in transforming the battery industry.
Several digital product passport approaches are expected to be relevant for the automotive industry. The nearest and most prominent example is the Battery Passport, based on the renewed EU Battery Regulation. It affects all electric vehicles with a high-voltage battery of 2 kWh capacity, sold in the European Union from 2027 onwards.
With a similar timeframe, the Environmental Vehicle Passport is expected, which as measure of the new EU Regulation on Type-Approval of Motor Vehicles (known as Euro 7), will redefine the scope of emission and approval data that carmakers must provide to customers.
Even more important is the Circularity Vehicle Passport, expected for 2032.
The proposal for a regulation on automotive circularity requirements
The Circular Vehicle Passport represents a groundbreaking approach to sustainability, revolutionizing the way we perceive and manage the lifecycle of vehicles. As the automotive industry embraces circular economy principles, the Circularity Vehicle Passport emerges as a pivotal document, enabling the efficient reuse, recycling, and repurposing of vehicles, thereby reducing waste, and minimizing environmental impact. (5)
The proposal by the European Union regarding the regulation on management of end-of-life vehicles, which is currently under evaluation, aims on driving circularity within the automotive industry. It focuses on six key action fields (4):
Design Circular
Improve the rules on how cars must be designed to be easily dismantled for later remanufacturing or material recycling.
Used recycled content
25% of the plastic used to build a new vehicle should be secondary material.
Collect more and smarter
Reduce the number of end-of-life vehicles gone missing, enforce rules for monitoring and increase transparency.
Treat better
Recover more and better-quality raw materials by improving recycling processes and promoting reuse strategies.
Make producers responsible
Stricter governance, improved cooperation, increased circularity.
Cover more vehicles
Gradually extend the scope of the rules, e.g. to commercial vehicles and road bikes (1).
By 2035, the regulation should lead to:
The Circularity Vehicle Passport as the digital enabler
To enforce the regulation and to reach the targets, a Circularity Vehicle Passport is stated as the digital enabler. It serves as a comprehensive, digital record that provides detailed information about a product's design, manufacturing, materials, and environmental impact, facilitating transparency, traceability, and sustainable practices throughout its lifecycle. Following more prominent solutions such as the Battery Passport or the Circularity Vehicle Passport may include:
- Material data, such as the composition of the vehicle, the weight of the materials used and their origin.
- Dismantling information, such as disassembly instructions, and recycling recommendations. (3)
Our take on the Circularity Vehicle Passport
The current regulation is still in its infancy and has not passed the proposal stage yet. Until now, there has been no official timeline set for the implementation of the regulation, neither have detailed information on the contents of the Circularity Vehicle Passport been defined. However, at Siemens Advanta Consulting, we believe that this or similar regulations will certainly become reality in the near future, following the landmarks of the European Green Deal. For the Circularity Vehicle Pass, we expect the corresponding regulation to enter into force in the beginning of the next decade. Therefore, we recommend automotive OEMs to engage in thought leadership and drive the development of an infrastructure which can enable digital product passports. Pioneers will further have the chance to push own standards in the market and actively collaborate on the development of industry standards. We also believe that those who go ahead now, can leverage considerable synergies from existing or planned digital product passports, such as the Battery Passport. Ultimately, just like the latter mentioned, the Circularity Vehicle Passport may also enable internal use cases for manufacturers to save costs, improve quality, or facilitate new business models and customer features.
With deep expertise in supporting external clients in the setup of already existing product passports, Siemens Advanta Consulting is your expert in the fast paced and constantly changing world of digital product passports. We are happy to guide you on your way towards a more sustainable future by using such digital tools, from the initial exploration of a fitting solution for you until the integration of the solution. We look forward to helping you close the loop and stepping into a bright circular future.
Our industry leader

- European Commission - Press release; Circular economy: improving design and end-of-life management of cars for more resource-efficient automotive sector; Brussels, 13 July 2023
- End-of-life vehicles Regulation (europa.eu)
- Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL on circularity requirements for vehicle design and on management of end-of-life vehicles, amending Regulations (EU) 2018/858 and 2019/1020 and repealing Directives 2000/53/EC and 2005/64/EC; (Text with EEA relevance) {SEC(2023) 292 final} - {SWD(2023) 255 final} - {SWD(2023) 256 final} - {SWD(2023) 257 final}; Brussels, 13.07.2023
- COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT; Subsidiarity Grid; Accompanying the document
Proposal for a REGULATION OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL on circularity requirements for vehicle design and on management of end-of-life vehicles, amending Regulations (EU) 2018/858 and 2019/1020, repealing Directives 2000/53/EC and 2005/64/EC; {COM(2023) 451 final} - {SEC(2023) 292 final} - {SWD(2023) 256 final} - {SWD(2023) 257 final}; Brussels, 13.07.2023 - COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT; IMPACT ASSESSMENT REPORT; Accompanying the document Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on circularity requirements for vehicle design and on management of end-of-life vehicles, amending Regulations (EU) 2018/858 and 2019/1020 and repealing Directives 2000/53/EC and 2005/64/EC; {COM(2023) 451 final} - {SEC(2023) 292 final} - {SWD(2023) 255 final} - {SWD(2023) 257 final}; Brussels, 13.07.2023
- COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT; IMPACT ASSESSMENT REPORT; ANNEXES 10 TO 15 to the IMPACT ASSESSMENT REPORT; Accompanying the document; Proposal for a Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council on circularity requirements for vehicle design and on management of end-of-life vehicles, amending Regulations (EU) 2018/858 and 2019/1020 and repealing Directives 2000/53/EC and 2005/64/EC; {COM(2023) 451 final} - {SEC(2023) 292 final} - {SWD(2023) 255 final} - {SWD(2023) 257 final}; Brussels, 13.07.2023
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 3
- Next page





























 Contact Us
Contact Us